In mechanical systems where axial loads dominate and precise rotational alignment is essential, selecting the right type of thrust bearing is crucial. Among the most reliable options are ball thrust, banded thrust ball bearings, and bearing thrust ball types, which offer smooth axial support in compact and efficient designs. But not all thrust ball bearings function the same. The key distinction lies between single-direction and double-direction types—each with its own advantages, limitations, and best-fit applications. Know More
What Are Thrust Ball Bearings?
Thrust ball bearings are specialized components designed to support loads along the axis of a shaft rather than perpendicular to it. Unlike radial bearings that manage side forces, ball thrust bearings are purpose-built for axial (thrust) loads. Their design consists of:
- Two rings (washers): One fixed and one rotating
- Ball set: Positioned between the rings, transferring the axial load
- Cage: Keeps balls evenly spaced
In many designs, including the banded ball thrust bearing, the assembly is enclosed by a steel band to hold the parts together, simplifying handling and installation.
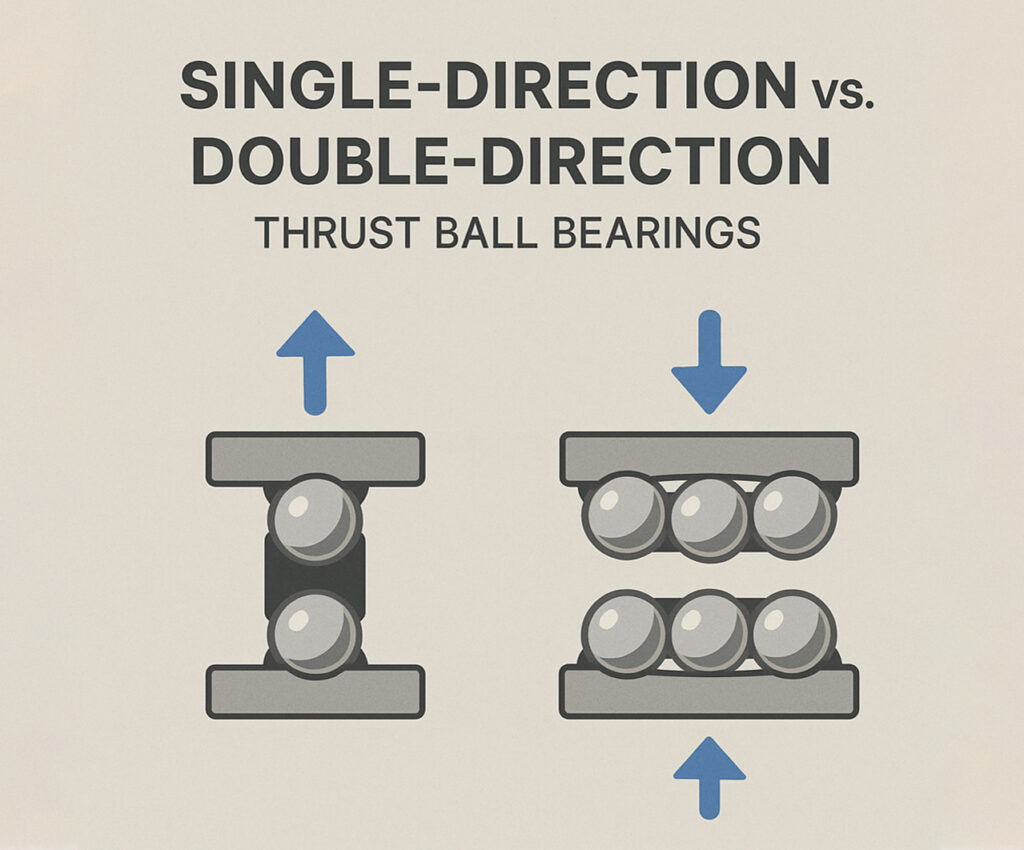
Single-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings
These bearings are designed to handle axial loads in only one direction. They cannot sustain radial loads or reverse thrust forces.
Structure:
- One shaft washer
- One housing washer
- One ball and cage assembly
Key Characteristics:
- Simple construction
- Cost-effective
- High precision in axial alignment
Use Cases:
- Automotive steering columns
- Light-duty jacks and lifts
- Machine tools
Because ball thrust bearings in a single-direction setup are limited to one axial direction, they’re best for systems where the load doesn’t change direction.
Double-Direction Thrust Ball Bearings
These bearings are designed to handle axial loads in both directions. They feature a more complex design but offer increased flexibility and support.
Structure:
- One shaft washer (central)
- Two housing washers (one on each side)
- Two ball and cage assemblies
Key Characteristics:
- Supports thrust in both axial directions
- Suitable for bidirectional loading applications
- Slightly more expensive but offers greater versatility
Use Cases:
- Vertical pumps
- Machine tool spindles with oscillating loads
- High-precision rotary tables
When a system experiences axial loads from both directions—such as vibration, back-and-forth motion, or shifting torque—bearing thrust ball designs in a double-direction configuration are the optimal choice.
Pros and Cons of Each Type
| Feature | Single-Direction Thrust Ball Bearing | Double-Direction Thrust Ball Bearing |
| Axial Load Direction | One direction only | Both directions |
| Radial Load Capability | None | None |
| Design Simplicity | Simple | Moderate complexity |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Fixed-load systems | Reversible-load systems |
| Alignment Tolerance | Tight | Moderate |
The Role of Banded Ball Thrust Bearings
A banded ball thrust bearing is essentially a thrust ball bearing enclosed with a band or steel ring. This design enhancement keeps all components tightly packed, making it easier to transport, install, and maintain. Banded designs are available in both single and double-direction variants.
Advantages of Banded Bearings:
- No component separation during handling
- Enhanced structural integrity
- Ideal for pre-assembled units and high-volume production
They’re commonly used in applications where installation speed and reliability are key—like automotive assembly lines or bulk machinery manufacturing.
Comparing Materials and Design Variants
Thrust ball bearings, including ball thrust and bearing thrust ball types, come in various material options depending on the application:
- Steel (standard): Great for general use and affordability
- Stainless steel: Offers corrosion resistance for marine or food-grade equipment
- Ceramic-hybrid: Ideal for high-speed, low-friction environments
Cages may be made from:
- Pressed steel (standard)
- Brass (better performance in higher temperatures)
- Polyamide (lightweight and quiet operation)
Choose based on environment, temperature, load, and speed requirements.
Lubrication Needs
Proper lubrication is vital to any bearing thrust ball system. Whether it’s oil or grease, maintaining a lubricated contact zone between balls and raceways helps prevent:
- Wear
- Overheating
- Friction-induced damage
Sealed variants, especially in banded ball thrust bearing configurations, come pre-lubricated and are often maintenance-free. For open systems, regular re-lubrication based on operational cycles is necessary.
Installation Tips for Maximum Performance
- Check for Alignment: Misalignment is a leading cause of early failure in ball thrust bearings.
- Apply the Correct Load: Exceeding the axial rating or introducing radial load can reduce life.
- Use the Right Preload: Especially in double-direction types, controlled preload ensures stable positioning and vibration resistance.
- Clean Assembly Environment: Contaminants in the raceway will drastically reduce lifespan.
Real-World Applications
Aerospace
Used in flap actuators and control systems where axial precision and load handling are critical.
Robotics
Double-direction bearing thrust ball units help manage complex multi-axis motion.
Renewable Energy
Thrust ball bearings in wind turbines manage axial loads from shaft movements and rotational friction.
Marine Equipment
Stainless or banded ball thrust bearings are found in propeller shafts and steering mechanisms.
Automotive Industry
Used in clutch assemblies and suspension systems, particularly banded ball thrust bearing types for quick assembly and rugged use.
Emerging Trends in Thrust Ball Bearing Design
- Sensor Integration: New designs include sensors that monitor load, temperature, and vibration.
- Advanced Coatings: DLC (diamond-like carbon) and ceramic coatings for reduced friction and wear.
- 3D-Printed Cages: Lightweight, custom-designed cages for specific motion profiles.
- Solid Lubricant Bearings: Bearings infused with graphite or PTFE for maintenance-free operations.
These innovations are expanding the scope and capabilities of both ball thrust and bearing thrust ball products in smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0 environments.
Choosing Between Single and Double-Direction Bearings
Ask the following before selecting:
- Will the axial load reverse? If yes, go with double-direction.
- Is cost a major factor? Single-direction bearings are typically more economical.
- Is assembly time limited? Consider a banded ball thrust bearing to speed things up.
- Do you need maintenance-free operation? Opt for sealed or pre-lubricated designs.
Final Thoughts
Whether your design calls for single-direction simplicity or double-direction flexibility, ball thrust bearings offer a proven solution for managing axial loads with precision. The choice between a banded ball thrust bearing or a more modular setup depends on your application’s complexity, cost, and maintenance profile.
In environments where reliability, speed, and precision matter, bearing thrust ball systems are the quiet force driving countless innovations—one axial revolution at a time.