In the world of rotating equipment, reliability starts with the right foundation—and that foundation often includes choosing the proper bearing housings. From standard industrial machines to custom-built motion systems, engineers must know how to match housing styles to application needs. Whether you’re working with pillow block bearings and shaft alignments, installing a pillow block flange bearing into a compact assembly, or exploring linear pillow block bearings for precision rail movement, understanding housing types is critical.
This guide explores the major bearing housing types—including P, F, FL, T styles—and explains how each one supports mechanical performance, alignment accuracy, and maintenance convenience. We’ll also break down typical applications, mounting formats, and how to choose the right housing for your system. Know More
What Is a Bearing Housing?
A bearing housing is a structural element that holds and supports a bearing while facilitating load transmission, alignment, and lubrication. Housings can be made from cast iron, pressed steel, stainless steel, or thermoplastics depending on the environment.
In setups using pillow block bearings and shaft systems, the housing plays a dual role: it provides a mounting platform and helps maintain shaft alignment across dynamic loads. These housings are often pre-drilled for easy installation and may include lubrication ports, drain plugs, or seals for contamination protection.
The Importance of Housing Selection
Choosing the right housing:
- Ensures proper alignment of the shaft and bearing
- Protects the bearing from contamination
- Supports static and dynamic loads
- Enables fast maintenance or replacement
When integrated with components like pillow block flange bearing units or linear pillow block bearings, the housing can also contribute to axial guidance, corrosion resistance, and thermal management.
Overview of Popular Housing Styles
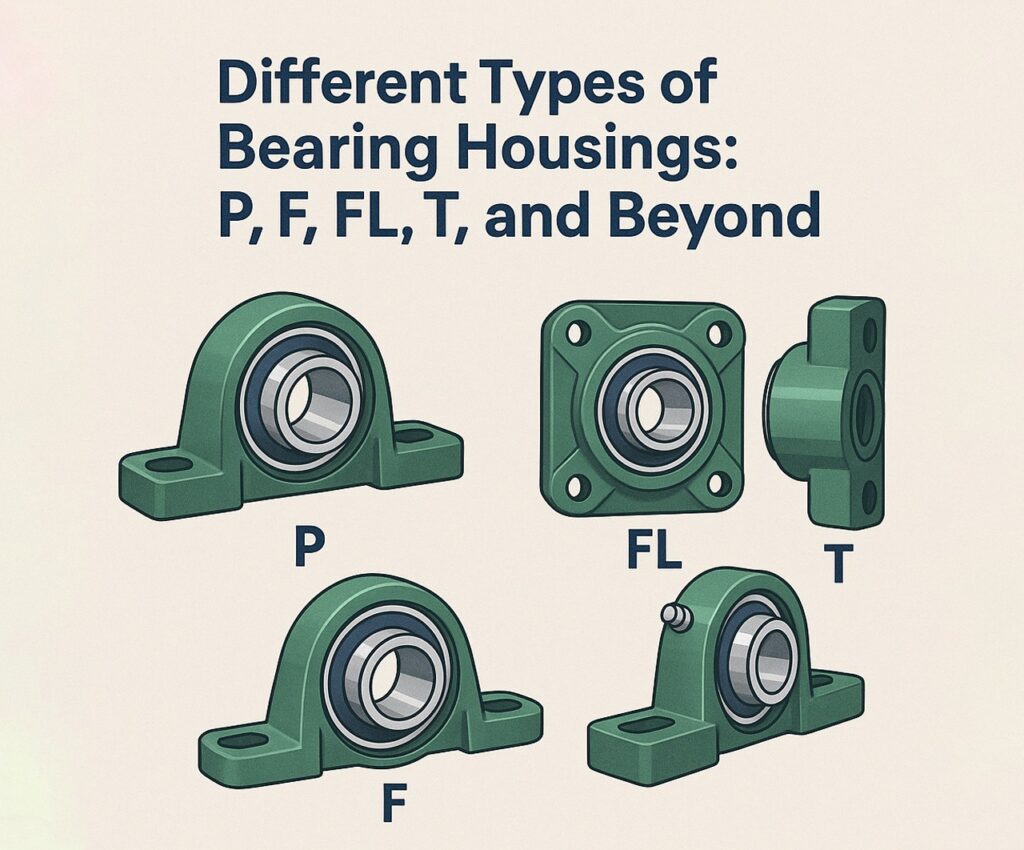
1. P-Type (Pillow Block)
Pillow block bearings and shaft combinations are widely used in general machinery, HVAC systems, and conveyor lines. The P-type housing supports the bearing from below and includes two mounting bolts that secure it to a base surface.
Features:
- Horizontal mounting
- Self-aligning insert bearings
- Built-in lubrication channels
Applications:
- Agricultural equipment
- Fan drives
- Roller beds
2. F-Type (Flange Housing)
The pillow block flange bearing style is typically used where the shaft is perpendicular to the mounting surface. F-housings usually have four mounting holes and are ideal for vertical walls or machine panels.
Features:
- Flat or raised mounting face
- Often paired with wide inner ring bearings
- Supports axial and radial alignment
Applications:
- Food processing machinery
- Pump and mixer supports
- Wall-mounted drives
3. FL-Type (2-Bolt Flange)
A more compact variant of the F-type, the FL housing uses two bolts in a triangular arrangement. This is perfect for limited-space setups requiring easy assembly and disassembly.
Key Attributes:
- Lightweight and easy to mount
- Often used with thermoplastic or stainless options
- Supports moderate radial loads
Applications:
- Textile machinery
- Packaging systems
- Vibration-prone environments
4. T-Type (Take-Up Unit)
T-type housings are designed to allow sliding movement of the shaft, commonly used in belt-tensioning applications. They’re mounted in take-up frames or slots and allow dynamic shaft positioning.
Key Benefits:
- Axial shaft adjustment
- Built-in lubrication paths
- Ideal for tensioning conveyors
Common Uses:
- Aggregate conveyors
- Belt-driven machines
- Dynamic positioning systems
5. L-Type (Cartridge Housing)
These cylindrical housings are designed for installation into a machined frame or plate. While not as popular as others, L-housings are used in customized setups requiring concentric bore alignment.
Attributes:
- Often paired with spherical bearings
- Allows press-fit or clamp-fit install
- Used in rotary equipment
Specialty Housing Configurations
Linear Pillow Block Bearings
Used in motion control systems, linear pillow block bearings support a shaft and allow for smooth linear travel with minimal friction.
Design Characteristics:
- Housed linear ball or bushing inserts
- Aluminum or polymer bodies
- Often used with rail systems
Ideal For:
- CNC machines
- 3D printers
- Automated assembly lines
Their ability to support both shaft alignment and mobility makes them a staple in precision engineering.
Split Housings
Split housings are used when large shaft diameters or high-load applications make installation difficult. The housing splits along a horizontal axis for easier access.
Advantages:
- Simplifies bearing replacement
- Excellent for heavy-duty loads
- Seals and cooling options available
Choosing the Right Housing: Key Considerations
- Mounting Orientation
- Vertical vs. horizontal surfaces
- Wall vs. base installations
- Environmental Exposure
- Corrosive chemicals, dust, or moisture?
- Use stainless steel or polymer housings if needed
- Load Direction
- Radial or axial emphasis?
- Consider self-aligning or fixed bearings accordingly
- Shaft Movement
- Is take-up or linear motion required?
- Choose T-type or linear pillow block bearings
- Maintenance Access
- Choose split housings for ease of maintenance
- Sealed units for remote or hard-to-reach locations
Comparing Housing Styles
| Housing Type | Mounting Style | Motion Type | Best For |
| P | Horizontal base | Fixed shaft | Conveyors, HVAC, general equipment |
| F | Vertical panel | Fixed shaft | Motors, mixers, compact machines |
| FL | Flat surface | Fixed shaft | Small machines, light loads |
| T | Slotted frame | Movable shaft | Conveyor tensioning, mining gear |
| L | Cartridge bore | Fixed shaft | Custom-built rotary equipment |
| Linear | Rail-mounted | Translational | CNC, robotics, printing |
Materials and Coatings
- Cast Iron: Standard for most industrial applications
- Thermoplastic: Ideal for food-grade or washdown environments
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant for marine and medical equipment
- Zinc-Plated Steel: Cost-effective for indoor/light-duty use
Many modern pillow block bearings and shaft configurations come with corrosion-resistant coatings or seals for extended life.
Installation Tips
- Pre-Align the Shaft
- Use laser or dial tools for precision
- Lubricate Before Installation
- Especially for sealed or high-speed systems
- Torque Bolts Evenly
- Uneven mounting distorts housing geometry
- Use Threadlock Where Needed
- Prevents bolt loosening in vibration-prone systems
- Check for Play or Misalignment
- Particularly with pillow block flange bearing installs on vertical surfaces
Common Failures and How to Avoid Them
- Overtightening: Can crack cast housings or distort insert alignment
- Misalignment: Shortens bearing life due to uneven loading
- Contamination: Causes premature failure; use sealed units in dirty environments
- Incompatible Materials: Results in corrosion or thermal expansion issues
Regular maintenance and proper selection ensure optimal performance, especially in critical linear pillow block bearings supporting automated systems.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the different types of bearing housings is essential for engineers, technicians, and plant managers alike. From standard pillow block bearings and shaft assemblies to advanced pillow block flange bearing and linear pillow block bearings used in robotic automation, the right housing ensures precision, reliability, and long-term cost savings.
Always consider application-specific needs—load direction, environmental conditions, maintenance access, and motion type—when choosing your bearing housing. A well-matched housing not only extends bearing life but also enhances system performance and safety.