Thrust ball bearings, also known in precision engineering circles as bearing ball thrust systems, are uniquely designed to manage axial loads with high efficiency. Among the various subtypes, angular contact thrust ball bearings stand out for their ability to handle both axial and light radial loads with remarkable speed and precision. Whether used in automotive gearboxes or high-speed turbines, these bearings are essential for smooth, axial-focused rotation under pressure. In this article, we’ll explore what makes them unique, how they function, and where they’re most effectively applied. Know More
What Are Thrust Ball Bearings?
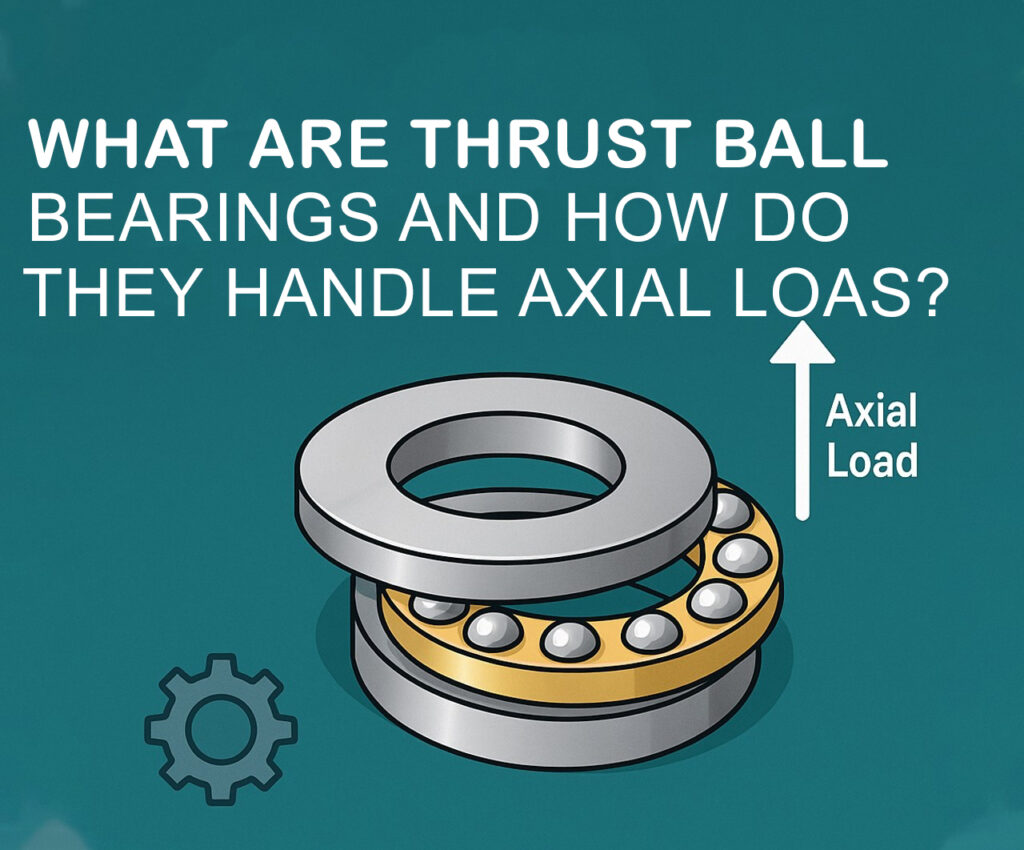
Thrust ball bearings are a special category of rotary bearings designed specifically to support loads parallel to the shaft, known as axial or thrust loads. They consist of ball bearings supported in a ring and are used in situations where axial loads are more significant than radial ones.
A basic bearing ball thrust unit comprises two washers—commonly called raceways—and a ball set held in a cage. One raceway is attached to the rotating shaft, while the other is stationary. The balls roll between the washers, supporting the axial force efficiently while reducing friction.
Types of Thrust Ball Bearings
There are several configurations of thrust ball bearings, each designed for different operational requirements:
- Single-direction thrust ball bearings: Can only support axial loads in one direction. Common in vertical shafts.
- Double-direction thrust ball bearings: Designed to carry axial loads in both directions. Useful in applications with reversing load direction.
- Angular contact thrust ball bearings: Unlike the standard models, these can handle a combination of axial and radial loads due to their unique raceway design. They are commonly used in high-speed and high-precision systems like aerospace and robotics.
The versatility of angular contact thrust ball bearings makes them a favorite in complex mechanical systems requiring both axial stability and speed.
How Do Thrust Ball Bearings Work?
The operation of bearing ball thrust systems is straightforward but effective. When an axial load is applied, it is transferred through the ball set from one washer to the other. Because the balls are rolling elements, they reduce the rotational friction significantly.
In angular contact thrust ball bearings, the contact angle of the raceways allows for better distribution of both radial and axial loads. This means they can support higher speeds and maintain alignment under fluctuating loads.
Materials and Design Innovation
Traditional thrust ball bearings are made from high-grade chrome steel, known for its strength and durability. For more demanding environments, stainless steel and ceramic hybrids are used. Ceramics are lighter and more heat-resistant, making them ideal for high-speed or high-temperature applications.
Modern bearing ball thrust units often feature:
- Polyamide cages: Lightweight and reduce friction.
- Black oxide coatings: For added corrosion resistance.
- Self-aligning designs: Which can accommodate misalignment in shaft positioning.
The design advancements in angular contact thrust ball bearings also include improved cage guidance and surface finishes that minimize vibration and noise.
Load Handling Capabilities
The primary role of thrust ball bearings is to manage axial loads. They are not designed to handle significant radial forces, except in the case of angular contact thrust ball bearings, which can accommodate minor radial loads due to the angled design of the contact surfaces.
- Axial Load: These bearings excel at supporting axial forces—forces that push or pull along the shaft direction.
- Combined Load: Angular contact thrust ball bearings can take on both axial and light radial forces, making them versatile.
Load capacity varies depending on bearing size, material, and design. Engineers must choose a bearing ball thrust system that matches the exact specifications of the mechanical application.
Applications of Thrust Ball Bearings
Thrust ball bearings are found in many mechanical systems that rely on precise axial load control:
- Automotive Transmissions: Manage gear thrust and alignment.
- Machine Tool Spindles: Provide stability under cutting forces.
- Electric Motors: Reduce axial play and improve rotor balance.
- Aerospace Systems: Use angular contact thrust ball bearings for lightweight, high-performance demands.
- Hydraulic Pumps and Compressors: Control axial loads from fluid pressure.
Each application benefits from the precision and low friction offered by modern bearing ball thrust designs.
Advantages of Thrust Ball Bearings
- High Axial Load Capacity: Specifically built for axial force management.
- Low Friction: Ensures smooth rotation and energy efficiency.
- Compact Design: Fits in tight spaces without compromising performance.
- High-Speed Operation: Especially true for angular contact thrust ball bearings.
- Customizability: Available in various materials and sizes to suit industry needs.
These features make thrust ball bearings a trusted component across many high-performance mechanical systems.
Maintenance and Reliability
Though relatively low-maintenance, bearing ball thrust units benefit from proper handling and upkeep:
- Lubrication: Essential for preventing wear and overheating. Grease or oil lubrication is common.
- Seal Integrity: Helps keep out contaminants and retain lubricants.
- Alignment: Improper shaft alignment can reduce bearing life, especially in angular contact thrust ball bearings.
- Load Monitoring: Overloading or incorrect force application can lead to premature failure.
Following best practices can significantly extend the service life of thrust ball bearings, especially in critical systems.
Emerging Innovations
Innovation in thrust ball bearings continues to evolve:
- Sensor Integration: Smart bearings with embedded sensors monitor load, temperature, and vibration.
- Advanced Lubricants: Self-lubricating materials that extend operational life.
- Miniaturization: Tiny bearing ball thrust models are now being used in micro-robotics and precision medical tools.
- Coated Bearings: Using nano-coatings to reduce surface wear and increase performance.
These trends are particularly noticeable in angular contact thrust ball bearings, which are often at the forefront of precision applications.
How to Choose the Right Thrust Ball Bearing
Selecting the right thrust ball bearings involves careful consideration:
- Load Type: Pure axial, or a combination of axial and radial?
- Speed Requirements: Higher speeds require lower friction and better materials.
- Environmental Conditions: Will the bearing face extreme temperatures or exposure to chemicals?
- Space Constraints: Ensure the size fits within design tolerances.
Using specification charts and manufacturer recommendations is key to selecting the most effective bearing ball thrust system for your project.
Conclusion
Thrust ball bearings are precision components engineered to handle axial loads with minimal friction and maximum reliability. Whether in industrial gearboxes or lightweight aerospace systems, they keep motion smooth and efficient. Bearing ball thrust designs vary from simple single-direction units to high-performance angular contact thrust ball bearings capable of managing complex load scenarios.
As machines become faster, smarter, and more compact, the demand for advanced thrust ball bearings will only grow. With ongoing innovation in materials, design, and monitoring technology, these bearings will continue to play a critical role in modern mechanical systems.